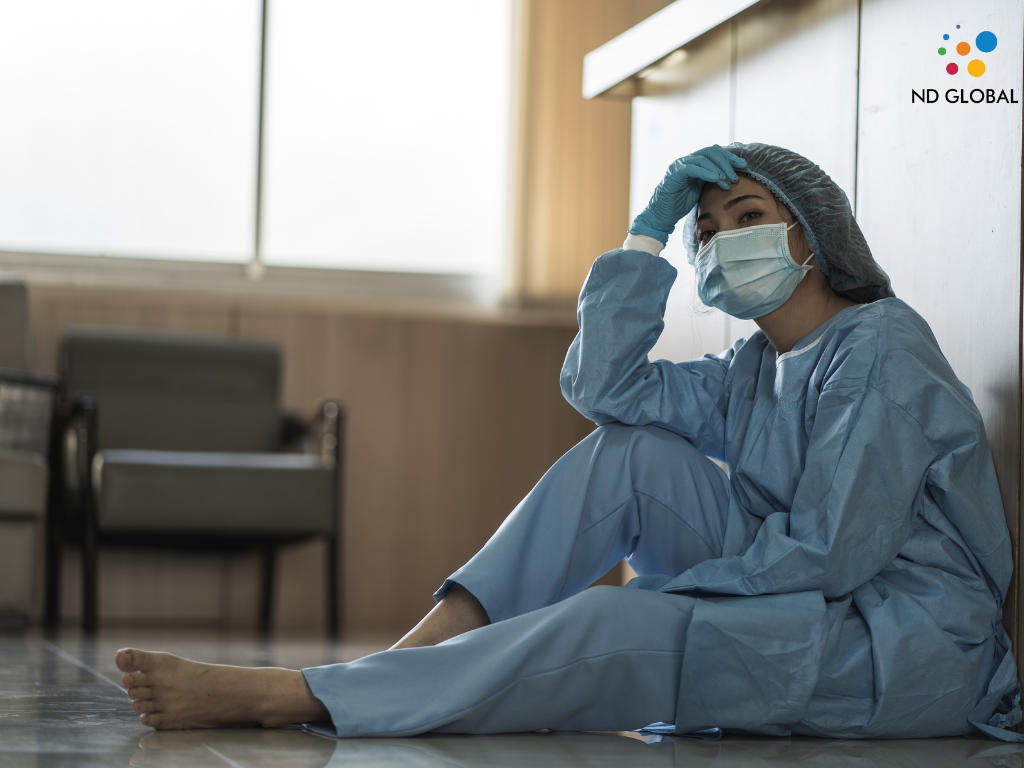
Burnout is a critical issue in the healthcare industry, affecting both the well-being of healthcare professionals and the overall quality of patient care. Defined by the World Health Organization as a syndrome resulting from chronic workplace stress that has not been successfully managed, burnout is characterized by feelings of energy depletion, increased mental distance from one’s job, and reduced professional efficacy. The impact of burnout on healthcare staffing is profound, leading to higher turnover rates, decreased patient satisfaction, and increased operational costs. This blog post explores the causes and consequences of burnout in healthcare and offers solutions to mitigate its impact.
Causes of Burnout in Healthcare
Several factors contribute to the high rates of burnout among healthcare professionals:
- Workload and Long Hours:
– High Patient Loads: Nurses, doctors, and other healthcare workers often handle high patient volumes, leading to physically and emotionally taxing workdays.
– Extended Shifts: Many healthcare providers work long hours, including overnight shifts, which disrupt sleep patterns and reduce the opportunity for rest and recovery.
- Emotional Stress:
– Patient Outcomes: The emotional toll of dealing with severe illnesses, trauma, and death can weigh heavily on healthcare providers.
– Patient and Family Interactions: Constantly managing the expectations and emotions of patients and their families adds to the stress.
- Administrative Burden:
– Documentation Requirements: Extensive documentation and compliance requirements can take time away from patient care and add to the workload.
– Bureaucratic Tasks: Healthcare providers often spend significant time on non-clinical tasks, which can be frustrating and lead to feelings of inefficiency.
- Work Environment:
– Staffing Shortages: Insufficient staffing levels mean that existing staff must take on additional responsibilities, leading to overwork.
– Lack of Support: Inadequate support from management and insufficient resources can exacerbate stress and burnout.
Consequences of Burnout on Healthcare Staffing
Burnout has far-reaching effects on healthcare staffing and the overall healthcare system:
- High Turnover Rates:
– Increased Resignations: Burned-out employees are more likely to leave their positions, leading to high turnover rates. This not only affects the continuity of care but also increases recruitment and training costs for healthcare facilities.
– Early Retirement: Experienced professionals may choose to retire early due to burnout, leading to a loss of valuable knowledge and expertise.
- Decreased Quality of Care:
– Medical Errors: Burnout can impair cognitive function and decision-making abilities, increasing the likelihood of medical errors and adverse patient outcomes.
– Patient Satisfaction: Patients may perceive the effects of burnout through decreased empathy and engagement from healthcare providers, leading to lower patient satisfaction scores.
- Impact on Team Dynamics:
– Morale and Collaboration: Burnout can negatively impact team morale and collaboration. Stressed and fatigued workers are less likely to communicate effectively and work well together.
– Increased Absenteeism: Burned-out employees are more likely to take sick leave, further straining staffing levels and placing additional pressure on their colleagues.
- Operational and Financial Costs:
– Increased Recruitment Costs: High turnover rates necessitate continuous recruitment efforts, which are costly and time-consuming.
– Productivity Losses: Burnout leads to decreased productivity and efficiency, affecting the overall performance of healthcare facilities.
Solutions to Mitigate Burnout in Healthcare
Addressing burnout in healthcare requires a multi-faceted approach that includes organizational, managerial, and individual strategies:
- Improving Workload Management:
– Adequate Staffing: Ensuring sufficient staffing levels is crucial. This may involve hiring additional staff, utilizing temporary or per diem staff during peak times, and leveraging technology to optimize staffing schedules.
– Balanced Workloads: Equitably distributing workloads and avoiding excessive overtime can help prevent burnout. Implementing policies that cap the number of consecutive hours worked and ensure regular breaks is essential.
- Enhancing Support Systems:
– Mental Health Resources: Providing access to mental health services, including counseling and stress management programs, can help healthcare workers cope with the emotional demands of their jobs.
– Peer Support Programs: Establishing peer support groups where healthcare professionals can share experiences and strategies for managing stress can foster a sense of community and resilience.
- Reducing Administrative Burdens:
– Streamlined Documentation: Implementing electronic health records (EHR) systems and other technologies that reduce the time spent on paperwork can allow healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
– Delegating Non-Clinical Tasks: Utilizing administrative support staff to handle non-clinical tasks can reduce the burden on healthcare providers.
- Promoting Work-Life Balance:
– Flexible Scheduling: Offering flexible work schedules, such as part-time options, job sharing, and remote work where feasible, can help healthcare professionals achieve a better work-life balance.
– Encouraging Time Off: Promoting the use of vacation time and ensuring that healthcare workers take regular breaks can prevent burnout and promote overall well-being.
- Creating a Positive Work Environment:
– Recognition and Rewards: Regularly recognizing and rewarding the hard work and achievements of healthcare staff can boost morale and motivation.
– Open Communication: Fostering an environment where healthcare professionals feel comfortable voicing concerns and suggestions can lead to improvements in the workplace and reduce feelings of helplessness and frustration.
- Providing Professional Development:
– Continuous Education: Offering opportunities for professional development and continuing education can keep healthcare workers engaged and motivated.
– Career Advancement: Creating clear pathways for career advancement can provide healthcare professionals with goals and a sense of purpose, reducing the likelihood of burnout.
- Implementing Organizational Changes:
– Leadership Training: Training leaders and managers to recognize the signs of burnout and take proactive measures to address it can create a more supportive work environment.
– Organizational Culture: Promoting a culture that values employee well-being and prioritizes work-life balance can have a significant impact on reducing burnout.
Conclusion
Burnout in healthcare is a serious issue with profound implications for healthcare staffing, patient care, and the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. By understanding the causes and consequences of burnout, healthcare organizations can implement effective strategies to mitigate its impact. This includes improving workload management, enhancing support systems, reducing administrative burdens, promoting work-life balance, creating a positive work environment, providing professional development opportunities, and implementing organizational changes.
Addressing burnout is not only crucial for the well-being of healthcare professionals but also for maintaining high standards of patient care and operational efficiency. By taking a proactive and holistic approach to tackling burnout, healthcare organizations can create a more resilient, engaged, and effective workforce, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a stronger healthcare system.